Server Provisioners
A Server Provisioner is a script that is executed during the initial setup of a virtual server.
Provisioners can be written in a variety of programming or scripting languages, such as sh, Bash, zsh, Python, PowerShell, Batch, or clout-init yaml, depending on the operating system and use case.
Creating a Provisioner
Navigate to Server -> Provisioners and click the Create Provisioner button.
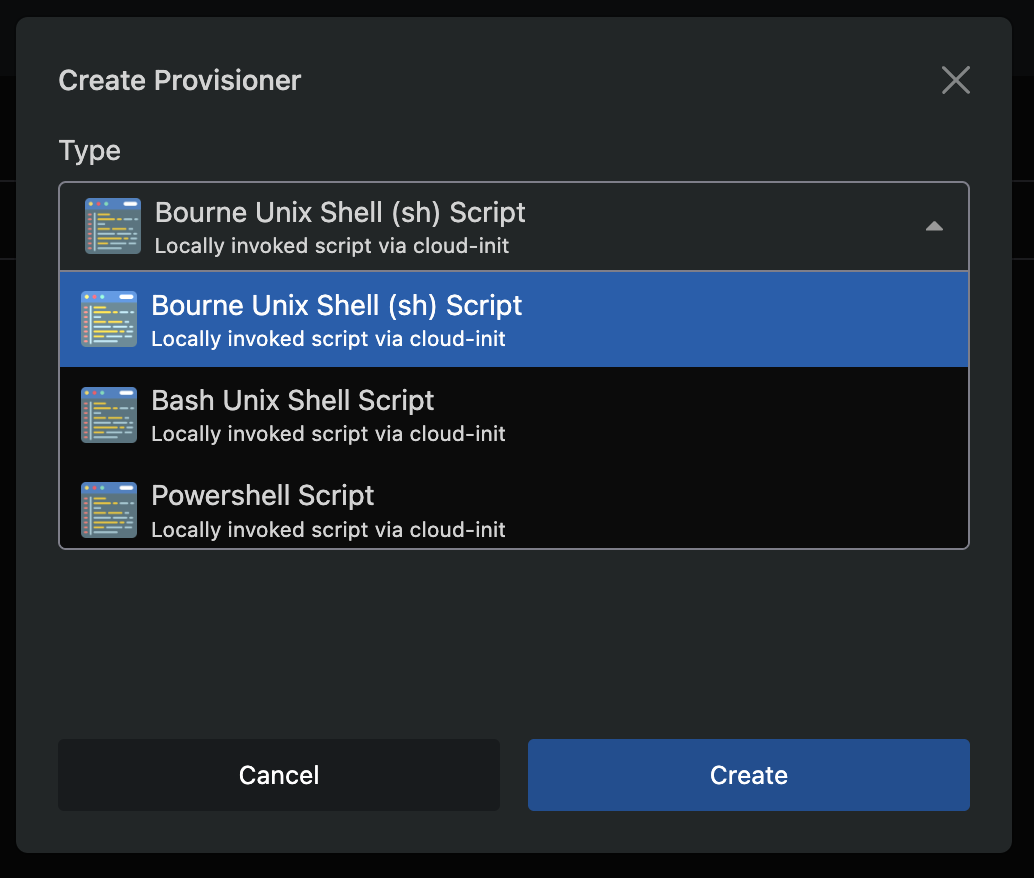
Select the provisioner Type and give it a Name. Then click the Create button.
On the next screen you can enter your script in the Script field. In this example (Bash) we will update the MOTD when a server is built.
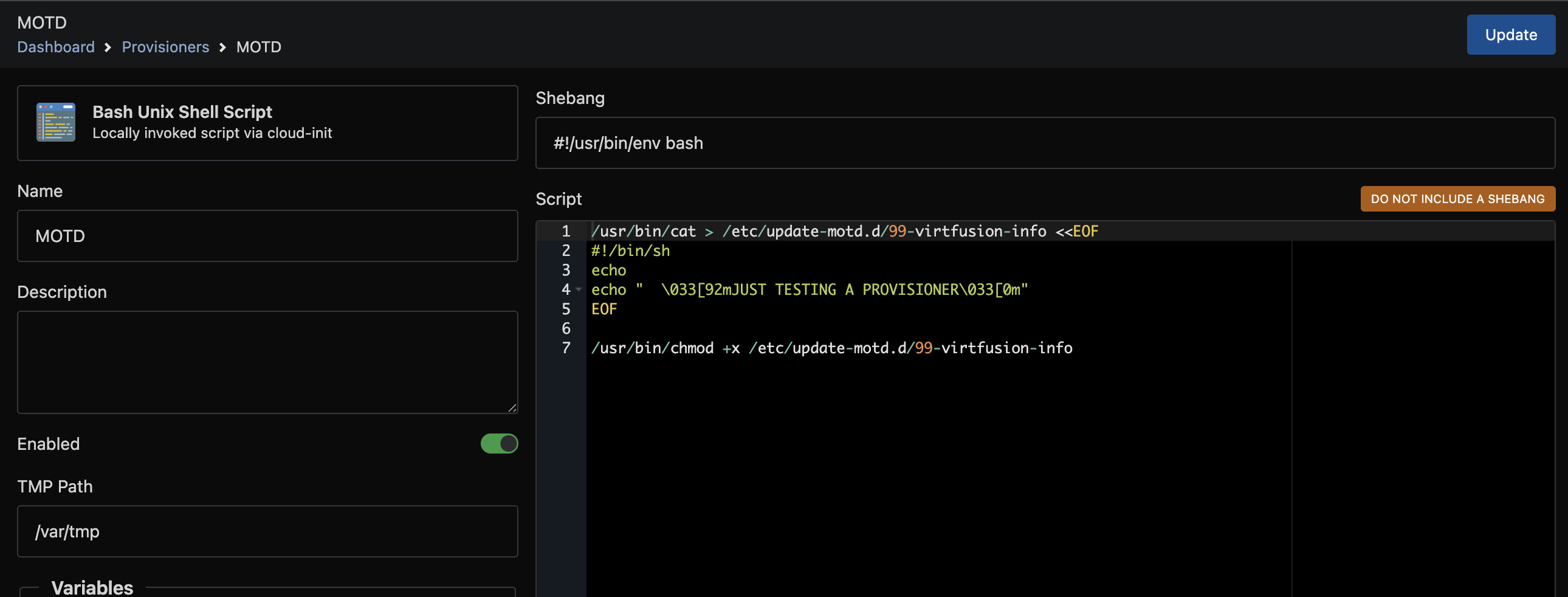
Here is a copy + pastable version of the example.
/usr/bin/cat > /etc/update-motd.d/99-virtfusion-info <<EOF
#!/bin/sh
echo
echo " \033[92mJUST TESTING A PROVISIONER\033[0m"
EOF
/usr/bin/chmod +x /etc/update-motd.d/99-virtfusion-info
On the same screen, there are a few other options.
Shebang- This will be applied to the beginning of the script. You should not need to change this.Description- A general description of the provisioner. It's just for reference.Enabled- Check or uncheck to enable or disable the provisioner.TMP Path- The temporary location the script will be stored before execution. You should not need to change this.Variables- A list of variables related to the server that will be available inside the script. TheAdd ALL variables to beginning of scriptoption will apply the variables to the top of the script for the specific language you are using.
When you have finished editing the provisioner, click the Update button.
Attaching a Provisioner to a Template
Navigate to Media -> Templates and select the template you would like to attach the provisioner to.
You will find a selectable list of provisioners in several sections. The most common choice is just after the Cloud Config (All) field.
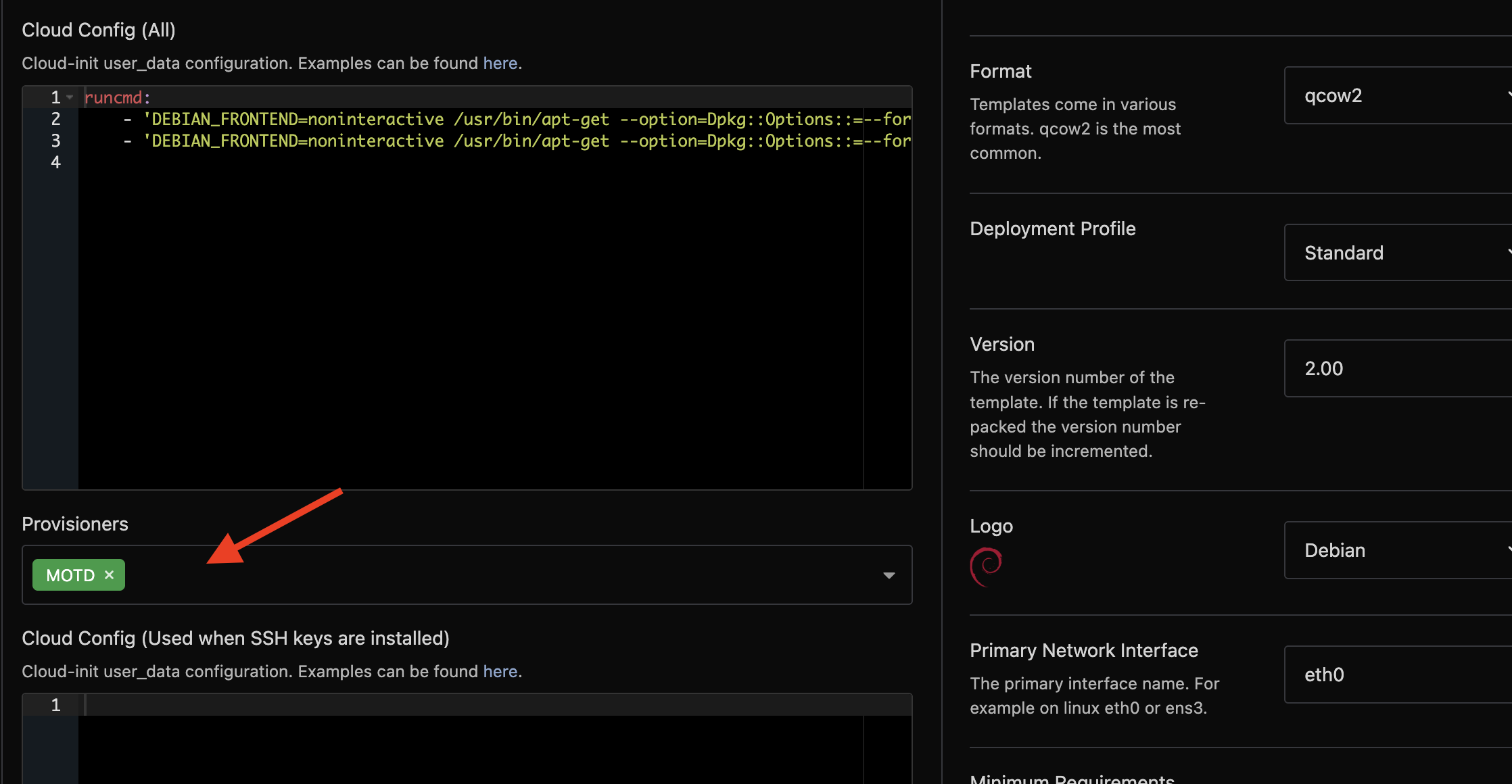
In this example we have attached the MOTD provisioner to the Debian 12 template. You can however clone a template and rename it.
Click the Update button to save your changes.
Using a Provisioner
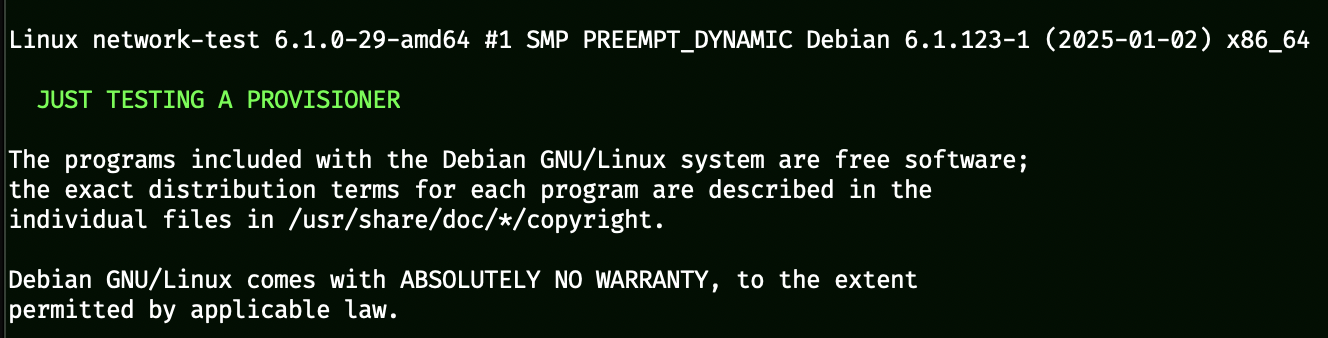
With a provisioner being attached to a template, there is nothing more to do. When a server is built with a template that has a provisioner attached, it will run automatically.
Based on our example provisioner. This is what we see when the server is built.
Debugging Provisioners
Provisioners are executed inside a server during its initial setup. Because of this, debugging provisioners can only be done from within the server after it has been built.
To troubleshoot or verify what happened during the provisioning process, you’ll need to access the server and review the following log files:
Linux & Unix
/var/log/cloud-init.log– Contains detailed logs of the provisioning process and any issues encountered./var/log/cloud-init-output.log– Captures the output of the scripts, which is useful for identifying script level errors or confirming successful execution.
Windows
C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\log\cloudbase-init
These logs provide insight into how the server was configured and can help identify problems with the provisioner script itself.